KOHLER'S DISEASE
THOMAS D. BECK JR., D.O., Resident Orthopaedic Surgery
J. RICHARD BOWEN , M.D., Attending Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgeon
May 28, 1996
CLINICAL CASE PRESENTATION
ORTHOPAEDIC DEPARTMENT
THE ALFRED I. DUPONT INSTITUTE
WILMINGTON, DELAWARE
CASE HISTORY:
Patient is a six year old male with a three week history of right foot
pain. Mother and patient relate no history of trauma. Patient came home
from school three weeks ago with pain and swelling over the medial aspect
of the right foot. Symptoms have persisted for past three weeks. Mother
states patient has been ambulating with a limp.
PHYSICAL EXAM : There is tenderness to palpation and minimal swelling
over the medial aspect of the right navicular. The lateral border of the
foot is straight without significant metatarsus adductus. The hindfoot
is supple and there is a normal arch. Examination of the left foot is unremarkable.
RADIOGRAPHS : AP, lateral and oblique views bilateral feet demonstrate
bilateral avascular necrosis of the navicular.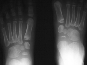
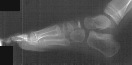
ASSESSMENT : Kohler's disease right foot.
TREATMENT : Patient was placed in a short leg walking cast on the right
for five weeks. Patient was asymptomatic after cast removal. Patient returned
to full activity and was still asymptomatic at return visit six weeks later.
Patient was to return on a PRN basis.
INTRODUCTION:
- osteochondrosis of the tarsal navicular
- described in 1908 by Kohler
- characterized by the radiographic findings of flattening, sclerosis
and irregular rarefaction
- more common in boys
- approximate age of onset :
- boys : 5 years
- girls : 4 years
- one third of cases have involvement of both feet
ETIOLOGY:
- the cause of Kohler's disease is unknown
- etiology may be mechanical
- result of repetitive compressive force
- navicular is the last bone in the foot to ossify
- irregularities of ossification are not uncommon and are more often
seen in :
- boys
- navicular which ossifies late
- Waugh
- serial radiographic study of normal children
- post- mortem injection studies naviculars of varying ages
- radiographic analysis of children with Kohler's disease
- conclusions :
- abnormal ossification results from compression of the bony nucleus
at a critical phase during growth of a navicular bone whose appearance
is delayed
- symptoms in Kohler's disease are related to further compression which
produces vascular changes in the bony nucleus, ischemia and pain
CLINICAL FEATURES
- limp ( may ambulate on lateral border of foot )
- pain and tenderness localized to region of the navicular
- swelling (may or may not be present )
- normal range of motion in the ankle and subtalar joints
RADIOGRAPHIC FINDINGS
- flattening of the navicular
- narrowing of the navicular AP diameter in the lateral view
- irregular rarefaction and sclerosis
- irregular ossification of the navicular is seen in normal feet
- diagnosis of Kohler's disease should only be made when symptoms are
present
TREATMENT
various treatment have been suggested
- skillful neglect
- shoe inserts
- rest
- casting
Williams and Cowell
- no difference in final outcome despite method of treatment
- type of treatment did effect duration of symptoms
- not casted
- asymptomatic in average of 15.2 months
- casted > 8 weeks
- asymptomatic in average of 2.5 months
- casted < 8 weeks
- asymptomatic in average of 4 months
LONG TERM RESULTS
Ippolito
- 12 patients with average of 33 year follow-up
- no symptomatic patients
- radiographically normal appearing navicular in an average of 8 months
- independent of the type of treatment
- no patients with degenerative changes
Williams and Cowell
- 20 patients with average of 9.5 year follow-up
- all patients asymptomatic at follow-up
- no evidence of arthritis
- all patients had navicular with normal radiographic appearance
Borges, Guille and Bowen
- 14 patients with average of 31.5 year follow-up
- 12 asymptomatic, 2 symptomatic
- symptomatic patients
- one patient with flatfoot and an accessory navicular
- one patient with tarsal coalition and degenerative changes
- patients with continued symptoms should be carefully examined for other
causes of pain
REFERENCES:
- Borges, et al. : Kohler's Bone Disease of the Tarsal Navicular. JPO
15:596-598, 1995.
- Ippolito, et al. : Kohler's Disease of the Tarsal Navicular : Long-Term
Follow-up of 12 Cases. JPO 4:416-417, 1984.
- Karp : Kohler's Disease of the Tarsal Scaphoid. JBJS 19:84-96, 1937.
- Morrissy and Weinstein : Lovell and Winter's Pediatric Orthopaedics
: Volume II, p.1101, Fourth Edition
- Siffert : Classification of the Osteochondroses. CORR 158: 10-18, 1981.
- Waugh : The Ossification and Vascularization of the Tarsal Navicular
and Their Relation to Kohler's Disease. JBJS 40-B:765-777, 1958.
- Williams, et al. : Kohler's Disease of the Tarsal Navicular. CORR 158:
53-58, 1981.



