

TEST Passive ROM Strength Spasticity Motor Control Comments
Rt LT Rt LT Rt LT Rt LT
Hip Flexion 120 115 4 5 1 1 yes yes
hip abduction (EXT 25 22 4 3 4 0 yes yes
KN))
Hip extension 8 0 5 5 yes yes
Hip Int Rotation 40 55
(EXT)
Hip ext Rotation 25 15
(EXT)
Thomas test 23 18
Knee extension -9 5 5 5 4 3 yes yes Rectus spasticity
Knee Flexion 135 145 5 4 1 2 yes yes
Knee reflex 2 3
Popliteal angle 70 70
Ely Test 85 85
Ankle Dorsiflexion 8 0 With knee Flexion
Ankle dorsiflexion 3 -10 5 4 yes no With Knee
Extension'
Ankle Plantar 35 50 4 5 3 1 yes yes
flexion
Foot inversion 45 40 5 5 3 3 yes yes Tibialis
Posterior
Foot eversion 33 -5 5 5 yes yes Perineals
Thigh Foot angle e-35 e-10 done with knee
flexed
Babinski no no
Clonus 5 12
bts bts
Standing GMFM 32 of 36
possible points
Leg length measured 87.5 87 Measured supine
The major findings on the kinematic were slow speed, normal cadence, and symmetrical but short step lengths.
Characteristic: Trial Normal % Normal TEMPORAL CHARACTERISTICS: Velocity, cm / sec 91.3 120.0 76.1 Cadence, steps / min 118.0 122.0 96.7 Stride Time, sec 1.0 1.0 101.7 SPATIAL CHARACTERISTICS: Stride Length, cm 92.8 119.0 78.0 Right Step Length, cm 47.7 59.4 80.3 Left Step Length, cm 45.1 59.4 76.0 Step Width, cm 17.1 12.0 142.7 Pelvic Width / Ankle Spread Ratio 0.98 2.0 48.9
The pelvis was rotated leading with the right forward 5 to 30 degrees
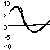 .
The left hip was adducted 5 to 25 degrees and internally rotated 20 degrees.
the right was externally rotated 10 degrees
.
The left hip was adducted 5 to 25 degrees and internally rotated 20 degrees.
the right was externally rotated 10 degrees 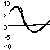 .
The right knee had increased mid-stance flexion of 30 degrees and good
flexion in swing. The left had flatted and decreased swing flexion and
both had increased knee flexion at foot contact at 35-40 degrees. The right
tibia demonstrated valgus of 25 degrees and external rotation of 20 degrees.
Dorsiflexion of the right ankle was good but plantar flexion was limited
to neutral. The left had limited dorsiflexion coming only to neutral. Foot
progression on the right was external 20-30 degrees and on the left was
internal 5 degrees
.
The right knee had increased mid-stance flexion of 30 degrees and good
flexion in swing. The left had flatted and decreased swing flexion and
both had increased knee flexion at foot contact at 35-40 degrees. The right
tibia demonstrated valgus of 25 degrees and external rotation of 20 degrees.
Dorsiflexion of the right ankle was good but plantar flexion was limited
to neutral. The left had limited dorsiflexion coming only to neutral. Foot
progression on the right was external 20-30 degrees and on the left was
internal 5 degrees 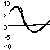 .
.
The recording of the Rectus muscle shows significant swing phase activity
bilaterally and very minimal stance activity. Both hamstring muscles show
significant constant activity but do have additional activity early stance
phase![]() . Tibialis anterior muscle has predominantly early swing phase activity
with significant underlying constant activity. The right gastrocnemius
has predominantly stance activity with good late stance phase contraction.
The left gastrocnemius has no recognizable pattern
. Tibialis anterior muscle has predominantly early swing phase activity
with significant underlying constant activity. The right gastrocnemius
has predominantly stance activity with good late stance phase contraction.
The left gastrocnemius has no recognizable pattern ![]() .
.
![]()
![]() A
derotation osteotomy of the left femur is definately indicated.
A
derotation osteotomy of the left femur is definately indicated.
![]()
![]() The
right tibia has 35 degrees of external torsion which is a major cause of
the knee valgus. Both of these can be corrected through a proximal tibial
osteotomy.
The
right tibia has 35 degrees of external torsion which is a major cause of
the knee valgus. Both of these can be corrected through a proximal tibial
osteotomy.
![]()
![]() One
option would be to do a external rotation femoral osteotomy on the left
and a proximal tibial osteotmy on the right. It would be important to do
the femur first.
One
option would be to do a external rotation femoral osteotomy on the left
and a proximal tibial osteotmy on the right. It would be important to do
the femur first.
![]()
![]() Reconstruction
of the left hip to gain good reduction and acetabular coverage will require
a pelvic osteotomy like a Dega. The indication for reconstructing this
hip remain unclear.
Reconstruction
of the left hip to gain good reduction and acetabular coverage will require
a pelvic osteotomy like a Dega. The indication for reconstructing this
hip remain unclear.
![]()
![]() Based
on the data above this boy needs a tnedon achilles lengthening on the left
in addition to the right knee and left hip procedure. This is all that
will be needed at this surgical event.
Based
on the data above this boy needs a tnedon achilles lengthening on the left
in addition to the right knee and left hip procedure. This is all that
will be needed at this surgical event.
Go to General Orthopaedist Level Modules, Go to Question Module Home Page, Go to Case Presentation Home Page, Orthopaedic Department Home Page.